Description of the configuration options for the Exchange over the Internet feature in Outlook 2003
On This PageSUMMARYIn Microsoft Office Outlook 2003, you can use the Exchange
over the Internet feature with Remote Procedure Calls (RPC) using HTTP packets
to connect to Microsoft Exchange Server 2003 over the Internet without having
to use virtual private network (VPN) connections. The Exchange over the
Internet feature permits Outlook 2003 users to access their Microsoft Exchange
Server accounts from the Internet when they are traveling or are working
outside their organization's firewall. MORE INFORMATIONThere following list includes the requirements for the
Exchange over the Internet feature:
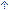
About the Exchange over the Internet FeatureIn a local area network (LAN), Outlook 2003 communicates with Exchange servers by using direct network TCP/IP access, also known as RPC over TCP/IP. This method provides both quick and efficient access to a corporate network. However, remote users who access Microsoft Exchange require a VPN connection that permits them to bypass the corporate firewall and to access the corporate network. A VPN connection permits access to more network services than those that are required for just e-mail access. Outlook 2003 now offers an alternative to VPN connections, the Exchange over the Internet feature. With the Exchange over the Internet feature, users can access their Exchange Server accounts from the Internet when they are working outside their organization's firewall. Users do not require any special connections or hardware, such as smart cards and security tokens, and they can still access their Exchange accounts even if the Exchange server and the client computer behind the firewall are on different networks. The Exchange over the Internet feature works by having an Exchange Server front-end computer that is configured as an RPC proxy server. This RPC proxy server specifies the ports that are used to communicate with the network's domain controller, the global catalog (GC) servers, and all the Exchange servers that the client user requires. Before you can use the Exchange over the Internet feature, the Exchange group in your organization must first deploy the Exchange over the Internet feature for the Exchange servers that you use. Understanding the Configuration Settings for the Exchange over the Internet FeatureBefore you configure the Exchange over the Internet feature for Outlook 2003, you have to have the Uniform Resource Locator URL) for the Exchange proxy server that is configured for the Exchange over the Internet feature. This URL is available from your organization's Exchange administrator.There are additional settings for the Exchange over the Internet feature in the Custom Installation Wizard (CIW). However, Outlook 2003 uses the default values for the options that are available in the CIW that are more likely to provide a good experience for your users and to help provide authenticated connections to your network. Microsoft recommends that you do not change the default options when you configure these settings in the CIW. However, if it is required, you can change these settings to fit the special circumstances in your organization. Overriding the Default Connection Type Choice BehaviorBy default, Outlook 2003 tries to connect by using the LAN connection first for a fast network . If you are using a slow network, Outlook 2003 tries to connect by using HTTP first. You can override these two default behavior following these steps:
Specifying Authentication and Connection MethodsThe default authentication method in the Exchange over Internet feature is through Password Authentication (NTLM). If you use Basic Password Authentication, users will be prompted for a password each time that a connection is made to the Exchange server. It is best to always use SSL while using password authentication. For additional recommendations about how to protect Exchange over the Internet connections, visit the MSDN Web site for the topic:http://msdn.microsoft.com/library/default.asp?url=/library/en-us/rpc/rpc/remote_procedure_calls_using_rpc_over_http.asp (http://msdn.microsoft.com/library/default.asp?url=/library/en-us/rpc/rpc/remote_procedure_calls_using_rpc_over_http.asp) REFERENCES For additional information about
how to obtain the hotfix 331320 and Windows XP Service Pack 1, click the
following article numbers to view the articles in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
331320 (http://support.microsoft.com/kb/331320/)
Outlook 2003 Performs Slowly or Stops Responding When Connected to Exchange Server 2003 Through HTTP
322389 (http://support.microsoft.com/kb/322389/) How to Obtain the Latest Windows XP Service Pack
| Search Support(KB)Article Translations
|
| ||||||
| Search Microsoft.com for: |